分析器概述
在文本处理中,分析器是将原始文本转换为结构化、可搜索格式的关键组件。每个分析器通常由两个核心元素组成:tokenizer 和 filter。它们一起将输入文本转换为 token,优化这些 token,并为高效索引和检索做好准备。
在 Milvus 中,分析器在创建 collection 时配置,当您向 collection schema 添加 VARCHAR 字段时。分析器产生的 token 可用于构建关键词匹配的索引,或转换为稀疏嵌入用于全文搜索。有关更多信息,请参阅文本匹配或全文搜索。
使用分析器可能会影响性能:
-
全文搜索: 对于全文搜索,DataNode 和 QueryNode 通道消费数据更慢,因为它们必须等待分词完成。因此,新摄取的数据需要更长时间才能可供搜索。
-
关键词匹配: 对于关键词匹配,索引创建也会更慢,因为需要在分词完成后才能构建索引。
分析器的组成
Milvus 中的分析器恰好由一个 tokenizer 和零个或多个 filter 组成。
-
Tokenizer:tokenizer 将输入文本分解为称为 token 的离散单元。这些 token 可以是单词或短语,具体取决于 tokenizer 类型。
-
Filter:Filter 可以应用于 token 以进一步优化它们,例如通过将它们转换为小写或删除常见单词。
Tokenizer 仅支持 UTF-8 格式。对其他格式的支持将在未来版本中添加。
下面的工作流程显示了分析器如何处理文本。
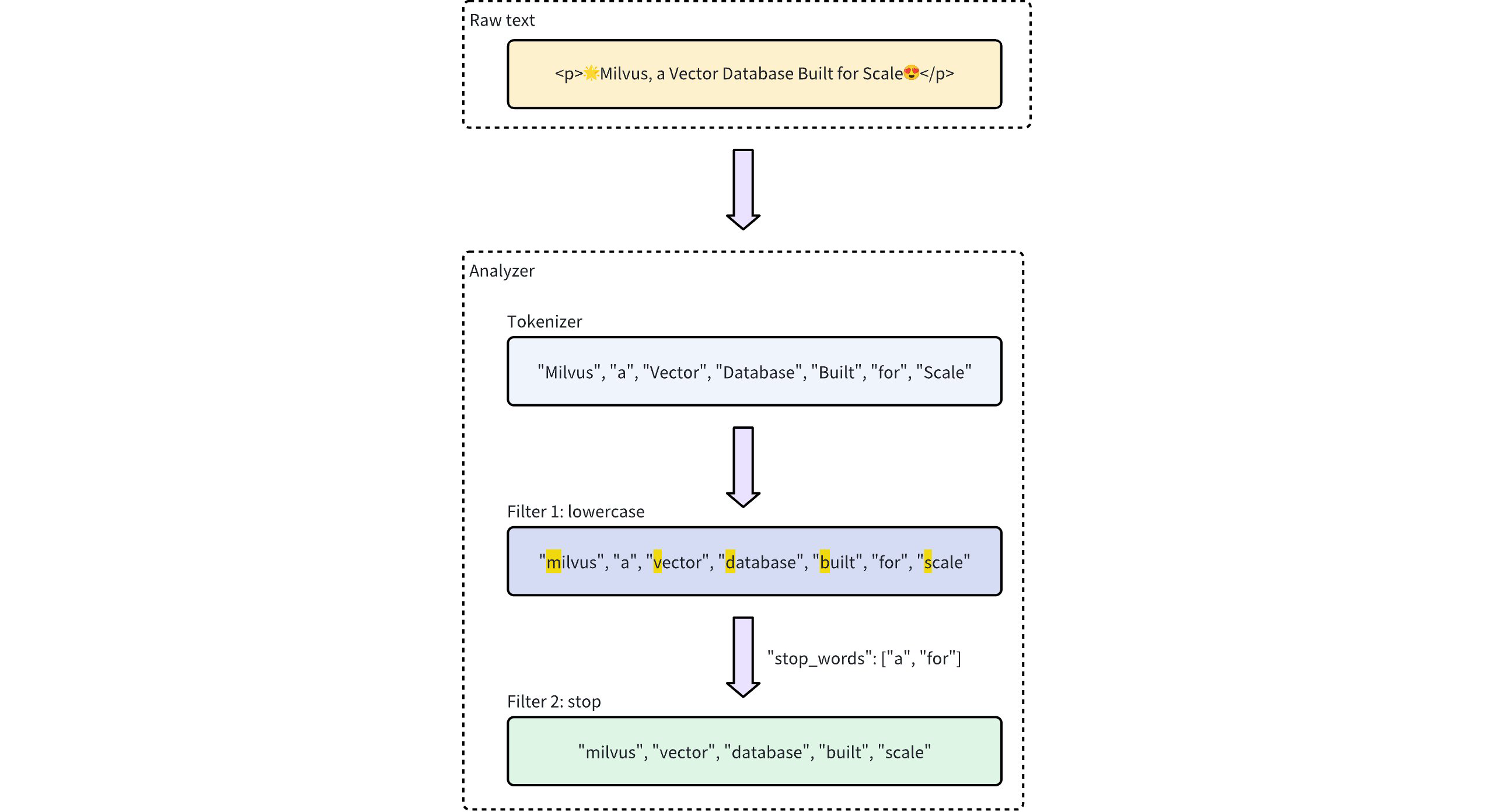
分析器类型
Milvus 提供两种类型的分析器来满足不同的文本处理需求:
-
内置分析器:这些是预定义的配置,以最少的设置涵盖常见的文本处理任务。内置分析器非常适合通用搜索,因为它们不需要复杂的配置。
-
自定义分析器:对于更高级的需求,自定义分析器允许您通过指定 tokenizer 和零个或多个 filter 来定义自己的配置。这种定制级别对于需要精确控制文本处理的专门用例特别有用。
如果您在创建 collection 时省略分析器配置,Milvus 默认使用 standard 分析器进行所有文本处理。有关详细信息,请参阅 Standard。
内置分析器
Milvus 中的内置分析器预配置了特定的 tokenizer 和 filter,允许您立即使用它们,而无需自己定义这些组件。每个内置分析器都充当包含预设 tokenizer 和 filter 的模板,并具有用于自定义的可选参数。
例如,要使用 standard 内置分析器,只需将其名称 standard 指定为 type,并可选择包含特定于此分析器类型的额外配置,例如 stop_words:
analyzer_params = {
"type": "standard", # Uses the standard built-in analyzer
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"] # Defines a list of common words (stop words) to exclude from tokenization
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("type", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
const analyzer_params = {
"type": "standard", // Uses the standard built-in analyzer
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"] // Defines a list of common words (stop words) to exclude from tokenization
};
analyzerParams := map[string]any{"type": "standard", "stop_words": []string{"a", "an", "for"}}
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}'
要检查分析器的执行结果,请使用 run_analyzer 方法:
# Sample text to analyze
text = "An efficient system relies on a robust analyzer to correctly process text for various applications."
# Run analyzer
result = client.run_analyzer(
text,
analyzer_params
)
// java
// javascript
// go
# restful
输出将是:
['efficient', 'system', 'relies', 'on', 'robust', 'analyzer', 'to', 'correctly', 'process', 'text', 'various', 'applications']
这表明分析器通过过滤掉停用词 "a"、"an" 和 "for",正确地对输入文本进行分词,同时返回其余有意义的 token。
上述 standard 内置分析器的配置等同于设置具有以下参数的自定义分析器,其中 tokenizer 和 filter 选项被明确定义以实现类似功能:
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Arrays.asList("lowercase",
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
}}));
const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
};
analyzerParams = map[string]any{"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": []any{"lowercase", map[string]any{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": []string{"a", "an", "for"},
}}}
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}'
Milvus 提供了以下内置分析器,每个设计用于特定的文本处理需求:
-
standard:适用于通用文本处理,应用标准分词和小写过滤。 -
english:为英文文本优化,支持英文停用词。 -
chinese:专门用于处理中文文本,包括适应中文语言结构的标记化。
Custom analyzer
对于更高级的文本处理,Milvus 中的自定义分析器允许您通过指定 tokenizer 和 filters 来构建自定义文本处理管道。这种设置对于需要精确控制的专门用例特别有用。
Tokenizer
Tokenizer 是自定义分析器的必需组件,它通过将输入文本分解为离散单元或 tokens 来启动分析器管道。标记化遵循特定规则,例如根据标记器类型拆分空格或标点符号。此过程允许对每个单词或短语进行更精确和独立的处理。
例如,标记器会将文本 "Vector Database Built for Scale" 分解为单独的标记:
["Vector", "Database", "Built", "for", "Scale"]
指定标记器的示例:
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "whitespace");
const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
};
analyzerParams = map[string]any{"tokenizer": "whitespace"}
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "whitespace"
}'
Filter
Filters 是可选组件,它们在工作流产生的标记上进行转换或优化,根据需要进行。例如,应用 lowercase 过滤器到标记化术语 ["Vector", "Database", "Built", "for", "Scale"] 后,结果可能是:
["vector", "database", "built", "for", "scale"]
自定义分析器中的过滤器可以是 内置 或 自定义,具体取决于配置需求。
-
内置过滤器:由 Milvus 预配置,需要最少的设置。您可以通过指定其名称来使用这些过滤器。以下过滤器是内置的直接使用:
-
lowercase:将文本转换为小写,确保不区分大小写匹配。有关详细信息,请参阅 Lowercase。 -
asciifolding:将非 ASCII 字符转换为 ASCII 等效字符,简化多语言文本处理。有关详细信息,请参阅 ASCII folding。 -
alphanumonly:仅保留字母数字字符,删除其他字符。有关详细信息,请参阅 Alphanumonly。 -
cnalphanumonly:删除包含任何非中文字符的标记,这些标记包含中文字符、英文字母或数字。有关详细信息,请参阅 Cnalphanumonly。 -
cncharonly:删除包含任何非中文字符的标记。有关详细信息,请参阅 Cncharonly。
使用内置过滤器的示例:
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", # Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": ["lowercase"], # Optional: Built-in filter that converts text to lowercase
}Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter", Collections.singletonList("lowercase"));const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", // Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": ["lowercase"], // Optional: Built-in filter that converts text to lowercase
}analyzerParams = map[string]any{"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": []any{"lowercase"}}export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
}' -
-
自定义过滤器:自定义过滤器允许进行专门配置。您可以通过选择有效的过滤器类型 (
filter.type) 并添加每个过滤器类型的特定设置来定义自定义过滤器。支持自定义的过滤器类型示例:-
stop:通过设置停止词列表(例如"stop_words": ["of", "to"])删除指定常用词。有关详细信息,请参阅 Stop。 -
length:根据长度条件排除标记,例如设置最大标记长度。有关详细信息,请参阅 Length。 -
stemmer:将单词简化为根形式,以实现更灵活匹配。有关详细信息,请参阅 Stemmer。
自定义过滤器配置示例:
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", # Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop", # Specifies 'stop' as the filter type
"stop_words": ["of", "to"], # Customizes stop words for this filter type
}
]
}Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Collections.singletonList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
}}));const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", // Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop", // Specifies 'stop' as the filter type
"stop_words": ["of", "to"], // Customizes stop words for this filter type
}
]
};analyzerParams = map[string]any{"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": []any{map[string]any{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": []string{"of", "to"},
}}}export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}' -
示例用法
在此示例中,您将创建一个包含以下内容的 collection 模式:
-
用于嵌入的向量字段。
-
两个用于文本处理的
VARCHAR字段:-
一个字段使用内置分析器。
-
另一个使用自定义分析器。
-
在将这些配置纳入您的 collection 之前,您将使用 run_analyzer 方法验证每个分析器。
步骤 1:初始化 MilvusClient 并创建模式
首先设置 Milvus 客户端并创建新模式。
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
# Set up a Milvus client
client = MilvusClient(uri="http://localhost:19530")
# Create a new schema
schema = client.create_schema(auto_id=True, enable_dynamic_field=False)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
// Set up a Milvus client
ConnectConfig config = ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("http://localhost:19530")
.build();
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(config);
// Create schema
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.enableDynamicField(false)
.build();
import { MilvusClient, DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
// Set up a Milvus client
const client = new MilvusClient("http://localhost:19530");
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/column"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/index"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/milvusclient"
)
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
cli, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: "localhost:19530",
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle err
}
defer client.Close(ctx)
schema := entity.NewSchema().WithAutoID(true).WithDynamicFieldEnabled(false)
# restful
步骤 2:定义并验证分析器配置
-
配置并验证内置分析器 (
english):-
配置:定义内置英文分析器的参数。
-
验证:使用
run_analyzer检查配置是否产生预期的标记化。
# Built-in analyzer configuration for English text processing
analyzer_params_built_in = {
"type": "english"
}
# Verify built-in analyzer configuration
sample_text = "Milvus simplifies text analysis for search."
result = client.run_analyzer(sample_text, analyzer_params_built_in)
print("Built-in analyzer output:", result)
# Expected output:
# Built-in analyzer output: ['milvus', 'simplifi', 'text', 'analysi', 'search']Map<String, Object> analyzerParamsBuiltin = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParamsBuiltin.put("type", "english");// Use a built-in analyzer for VARCHAR field `title_en`
const analyzerParamsBuiltIn = {
type: "english",
};analyzerParams := map[string]any{"type": "english"}# restful -
-
配置并验证自定义分析器:
-
配置:定义一个使用标准标记器和内置小写过滤器以及自定义过滤器(用于标记长度和停止词)的自定义分析器。
-
验证:使用
run_analyzer确保自定义配置按预期处理文本。
# Custom analyzer configuration with a standard tokenizer and custom filters
analyzer_params_custom = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase", # Built-in filter: convert tokens to lowercase
{
"type": "length", # Custom filter: restrict token length
"max": 40
},
{
"type": "stop", # Custom filter: remove specified stop words
"stop_words": ["of", "for"]
}
]
}
# Verify custom analyzer configuration
sample_text = "Milvus provides flexible, customizable analyzers for robust text processing."
result = client.run_analyzer(sample_text, analyzer_params_custom)
print("Custom analyzer output:", result)
# Expected output:
# Custom analyzer output: ['milvus', 'provides', 'flexible', 'customizable', 'analyzers', 'robust', 'text', 'processing']// Configure a custom analyzer
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Arrays.asList("lowercase",
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "length");
put("max", 40);
}},
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("of", "for"));
}}
)
);// Configure a custom analyzer for VARCHAR field `title`
const analyzerParamsCustom = {
tokenizer: "standard",
filter: [
"lowercase",
{
type: "length",
max: 40,
},
{
type: "stop",
stop_words: ["of", "to"],
},
],
};analyzerParams = map[string]any{"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": []any{"lowercase",
map[string]any{
"type": "length",
"max": 40,
map[string]any{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": []string{"of", "to"},
}}}# curl -
步骤 3:将字段添加到模式中
现在您已经验证了分析器配置,将它们添加到模式字段中:
# Add VARCHAR field 'title_en' using the built-in analyzer configuration
schema.add_field(
field_name='title_en',
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length=1000,
enable_analyzer=True,
analyzer_params=analyzer_params_built_in,
enable_match=True,
)
# Add VARCHAR field 'title' using the custom analyzer configuration
schema.add_field(
field_name='title',
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length=1000,
enable_analyzer=True,
analyzer_params=analyzer_params_custom,
enable_match=True,
)
# Add a vector field for embeddings
schema.add_field(field_name="embedding", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=3)
# Add a primary key field
schema.add_field(field_name="id", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True)
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("title")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.analyzerParams(analyzerParams)
.enableMatch(true) // must enable this if you use TextMatch
.build());
// Add vector field
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("embedding")
.dataType(DataType.FloatVector)
.dimension(3)
.build());
// Add primary field
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
// Create schema
const schema = {
auto_id: true,
fields: [
{
name: "id",
type: DataType.INT64,
is_primary: true,
},
{
name: "title_en",
data_type: DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true,
analyzer_params: analyzerParamsBuiltIn,
enable_match: true,
},
{
name: "title",
data_type: DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true,
analyzer_params: analyzerParamsCustom,
enable_match: true,
},
{
name: "embedding",
data_type: DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim: 4,
},
],
};
schema.WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("id").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeInt64).
WithIsPrimaryKey(true).
WithIsAutoID(true),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("embedding").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeFloatVector).
WithDim(3),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("title").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithMaxLength(1000).
WithEnableAnalyzer(true).
WithAnalyzerParams(analyzerParams).
WithEnableMatch(true),
)
# restful
步骤 4:准备索引参数并创建 collection
# Set up index parameters for the vector field
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(field_name="embedding", metric_type="COSINE", index_type="AUTOINDEX")
# Create the collection with the defined schema and index parameters
client.create_collection(
collection_name="my_collection",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
// Set up index params for vector field
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("embedding")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.COSINE)
.build());
// Create collection with defined schema
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
// Set up index params for vector field
const indexParams = [
{
name: "embedding",
metric_type: "COSINE",
index_type: "AUTOINDEX",
},
];
// Create collection with defined schema
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: "my_collection",
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams,
});
console.log("Collection created successfully!");
idx := index.NewAutoIndex(index.MetricType(entity.COSINE))
indexOption := milvusclient.NewCreateIndexOption("my_collection", "embedding", idx)
err = client.CreateCollection(ctx,
milvusclient.NewCreateCollectionOption("my_collection", schema).
WithIndexOptions(indexOption))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
# restful